Understanding the Thermal Conductivity of Materials: Key Factors and Measurements
The thermal conductivity of materials plays a crucial role in a wide range of scientific and engineering applications. Understanding this property is vital for designing efficient thermal systems, insulating materials, and managing heat transfer in various industries, including electronics, construction, and manufacturing. The ability of a material to conduct heat can significantly affect the performance and durability of products, making it essential to measure and analyze the thermal conductivity accurately.
Key factors influencing the thermal conductivity of materials include their composition, structure, and temperature. For instance, metals generally exhibit higher thermal conductivity due to their free-moving electrons, while insulating materials display low conductivity, limiting heat transfer. Additionally, factors such as porosity, density, and moisture content can alter a material's thermal behavior. Through precise measurements and a deeper understanding of these factors, researchers and engineers can tailor materials for specific thermal management applications, contributing to more energy-efficient solutions and advancements in technology.
In this overview, we will explore the essential concepts surrounding the thermal conductivity of materials, including measurement techniques and the significance of this property in various contexts. By gaining insight into the mechanisms that dictate thermal conduction, we can appreciate the intricate relationship between material selection and thermal performance, ultimately influencing design decisions in numerous fields.

Key Definitions and Concepts in Thermal Conductivity
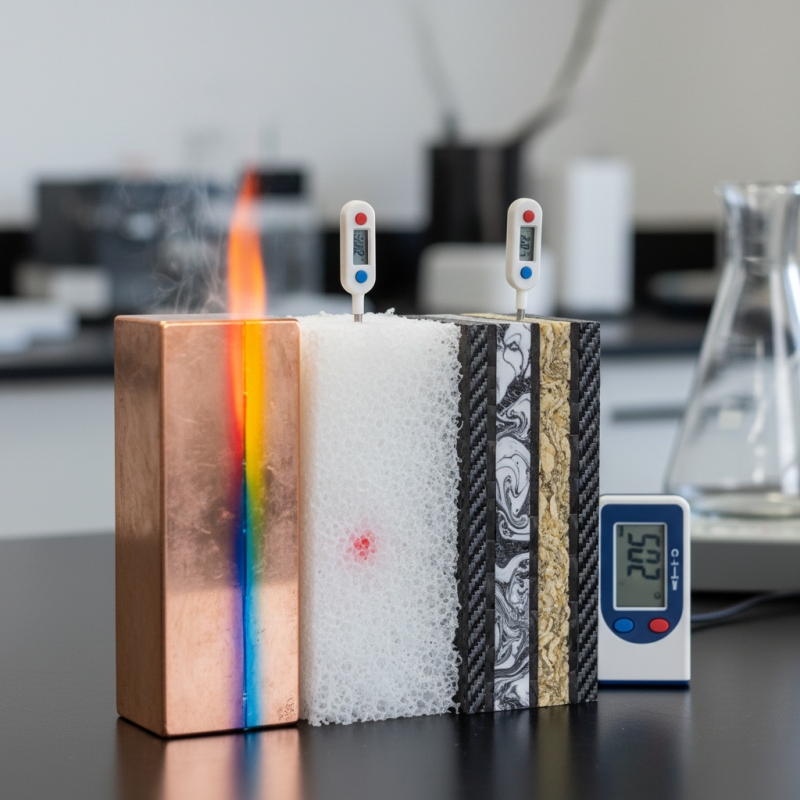
Thermal conductivity is a fundamental property of materials that describes their ability to conduct heat. It is influenced by several key factors, including the material's structure, temperature, and phase. In general, materials with closely packed atoms, such as metals, exhibit high thermal conductivity, while gases and some insulators have significantly lower values. Understanding these primary factors helps engineers and designers select appropriate materials for specific applications, from construction to electronics.
When measuring thermal conductivity, the technique used can greatly affect the results. Methods such as the guarded hot plate and laser flash analysis yield different insights into the material's heat transfer properties. These measurements are critical for evaluating performance in real-world conditions. Additionally, it is essential to consider environmental factors such as humidity and temperature variations since they can impact thermal conductivity.
Tip: When selecting materials for heat transfer applications, consider not just thermal conductivity but also other thermal properties like thermal diffusivity and heat capacity to get a comprehensive understanding of performance. Always conduct measurements under conditions that closely resemble the actual application to ensure accuracy.
Factors Influencing Thermal Conductivity of Materials
Thermal conductivity is a crucial property that influences the performance of materials in various applications, from construction to electronics. Several key factors dictate the thermal conductivity of a material, including its composition, structure, and temperature. For instance, metals typically exhibit high thermal conductivity due to the presence of free electrons that facilitate heat transfer. In contrast, insulating materials like ceramics or polymers have lower thermal conductivities because their molecular structures inhibit free electron movement.
Another significant factor is the temperature dependence of thermal conductivity. As temperature increases, the thermal conductivity of most materials also tends to rise, although this relationship can vary depending on the material type. According to industry reports, such as the “Thermal Conductivity of Materials” publication by the International Journal of Thermal Sciences, the thermal conductivities of common materials range from around 0.1 W/m·K for insulators to over 400 W/m·K for metals.
Tips: When selecting materials for high-temperature applications, consider those with increased thermal stability and lower thermal expansion coefficients to optimize performance. Additionally, for applications requiring insulation, prioritize materials with low thermal conductivity values to ensure efficiency. Understanding these factors can significantly enhance material selection and application outcomes.
Methods for Measuring Thermal Conductivity
Measuring the thermal conductivity of materials is essential for various applications in engineering, construction, and electronics. Several methods are employed to accurately determine this property, each with its advantages and limitations. The most commonly utilized techniques include steady-state methods, transient methods, and comparative methods, each suited for different types of materials and measurement conditions.
Steady-state methods involve maintaining a constant heat flow through a material while measuring the temperature gradient across it. Techniques such as the guarded hot plate and heat flow meters fall under this category. These approaches provide highly accurate results, particularly for bulk materials. In contrast, transient methods, like the laser flash analysis or transient plane source method, measure how a material's temperature changes over time after a brief heat pulse. These methods are particularly advantageous for thin films and small samples, offering rapid results with high sensitivity.
Comparative methods use a reference material with known thermal conductivity to evaluate the unknown sample's conductivity under similar conditions. This technique is often employed in industrial settings due to its simplicity and reliability. Each measuring method has its unique scope of applicability, and the choice depends on the material type, sample size, and required precision, thereby ensuring that developers can choose the most appropriate technique for their specific needs.
Applications of Thermal Conductivity in Various Industries
Thermal conductivity plays a crucial role across various industries, influencing the efficiency and performance of materials used in applications ranging from construction to electronics. In the construction industry, for instance, materials with low thermal conductivity are essential for achieving energy efficiency in buildings. According to a report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), improving insulation in buildings can reduce energy consumption by up to 30%, highlighting the importance of selecting materials with optimal thermal properties. This drives manufacturers to innovate and utilize materials such as aerogels and polyurethane foams that offer superior insulation capabilities.
In the electronics sector, understanding thermal conductivity is equally vital. As devices become more compact and powerful, managing heat dissipation is critical to maintaining performance and reliability. A study published in the Journal of Electronics Cooling and Thermal Control indicates that utilizing materials with high thermal conductivity—like copper and graphene—can enhance heat transfer efficiency, reducing the likelihood of thermal runaway in devices. This is particularly significant in LED technology and high-performance computing, where effective heat management systems can mean the difference between optimal functioning and failure.
Moreover, the automotive industry heavily relies on thermal conductivity to enhance the durability and performance of vehicles. Increasingly, electric vehicles (EVs) require advanced thermal management solutions to ensure battery efficiency and safety. According to the Automotive Research Association, implementing materials with excellent thermal properties can lead to a 15% increase in battery performance, directly impacting the range and longevity of EVs. These examples illustrate how optimizing thermal conductivity in various materials directly improves performance, safety, and energy efficiency across industries.
Recent Advances in Thermal Conductivity Research and Technology

Recent advancements in thermal conductivity research have opened doors to innovative materials with enhanced performance in various applications. Researchers are increasingly focusing on nanostructured materials and composites to improve thermal management in electronics, construction, and energy systems. These materials demonstrate superior thermal properties due to their unique microstructural features, allowing for improved heat dissipation and energy efficiency.
Tip: When evaluating materials for thermal conductivity, consider the microstructural design and processing techniques, as they significantly impact thermal performance.
Additionally, cutting-edge measurement techniques such as laser flash analysis and infrared thermography are being utilized to obtain accurate thermal conductivity data. These methods not only enhance the precision of measurements but also enable real-time monitoring of thermal performance under various conditions. This increasing reliance on advanced measurement techniques highlights the importance of understanding material behavior to drive innovations in technology.
Tip: To ensure accurate thermal conductivity assessments, prepare samples properly and select the right measurement method for the material type and application.
Related Posts
-

How to Select the Right Heat Flow Meter for Your Industrial Needs
-

10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Best Solar Irradiance Sensor in 2023
-

2025 Top 10 Temperature Sensors: The Best Choices for Precision and Performance
-

The Role of Solar Irradiance Sensors in Optimizing Renewable Energy Systems
-
Top 10 Temperature Probe Sensors for Accurate Cooking and Laboratory Use
-

7 Compelling Reasons Why a Soil Temperature Probe is Essential for Every Garden Enthusiast