Top 10 Heat Flux Transducers You Need to Know About?
In the realm of thermal measurement, heat flux transducers have emerged as critical tools for various industries. These devices quantify the rate of heat transfer, providing essential data for applications ranging from building energy efficiency to industrial processes. According to the "Global Heat Flux Sensor Market Report 2022," the industry is projected to grow at a rate of 8% annually, highlighting its increasing importance.
Dr. John Richards, a recognized expert in thermal dynamics, noted, "A precise understanding of heat transfer is indispensable for any thermal application." This highlights the necessity of utilizing high-quality heat flux transducers. However, the market is saturated with options, making the selection process challenging. Not all transducers are created equal, and performance inconsistencies can lead to significant measurement errors.
Industries must prioritize accuracy and reliability when choosing a heat flux transducer. Insufficient knowledge can lead to poor decision-making and flawed results. Thus, understanding the top heat flux transducers becomes essential for engineers and researchers aiming for precision in their thermal measurements.
Overview of Heat Flux Transducers: Definition and Importance
Heat flux transducers are essential devices in various engineering fields. They measure the flow of heat across surfaces. Understanding their function is important for energy efficiency and thermal management. These transducers help in optimizing systems, ensuring safety, and enhancing performance in processes.
Accurate heat flux measurements can lead to significant improvements. They can help in energy savings in buildings and industrial setups. However, selecting the right transducer can be challenging. Some models may not perform well in all conditions. Thus, careful consideration is necessary when choosing a device.
Tips: Always check the calibration of the transducer. A poorly calibrated device can result in faulty readings. Regular maintenance and testing are key for reliable data. Consider the environmental factors where the sensor will operate. Some may not withstand extreme temperatures or humidity levels.
Identifying the right heat flux transducer can make a difference. Not all transducers are created equal. Some might not fulfill your specific operational needs. Be prepared to invest time in research. Each application has unique requirements that should not be overlooked.
Key Specifications to Consider When Selecting Heat Flux Transducers
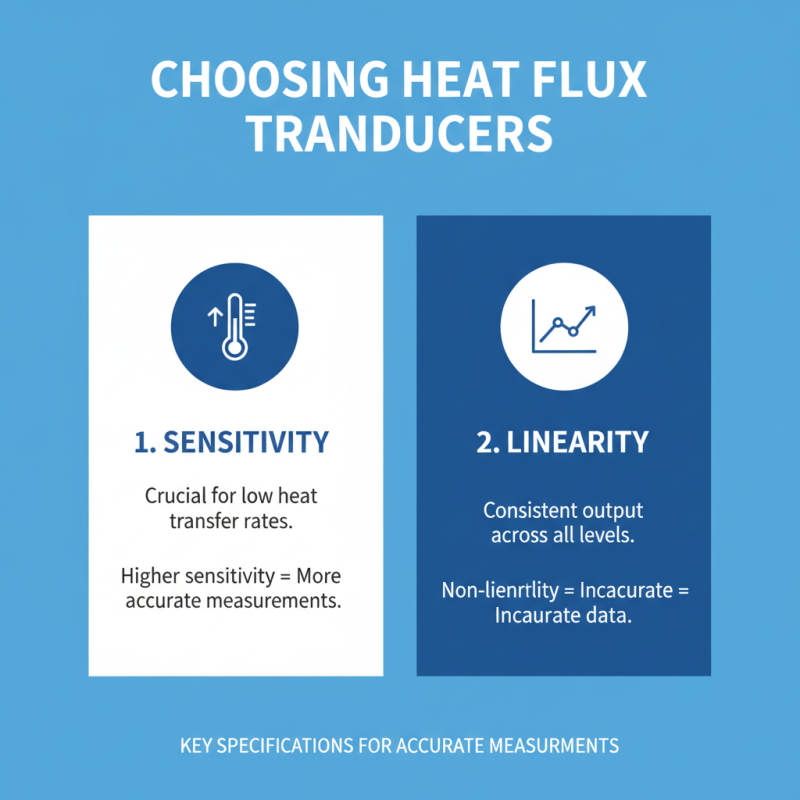
When choosing heat flux transducers, several key specifications stand out. Sensitivity is crucial. It indicates how responsive a transducer is to small changes in heat flux. Higher sensitivity allows for accurate measurements in environments where heat transfer rates are low. Moreover, linearity matters. A transducer should provide consistent output across a range of heat flux levels. Non-linearity can lead to data inaccuracies.
Temperature range is another critical aspect. Many applications involve extreme conditions. A transducer must withstand these without compromising performance. Additionally, measurement area size plays a role. A smaller measurement area can capture localized heat transfer effectively. Yet, it may miss broader trends.
Finally, consider the integration capability with existing systems. Some devices may require extensive modifications for compatibility. This can complicate implementation and lead to inefficiencies. Think about these factors carefully. They influence accuracy and reliability greatly. Adapting to specific needs can help find the right transducer.
Top 10 Heat Flux Transducers: Performance Metrics and Applications
Heat flux transducers are essential tools in thermal management and energy efficiency. They measure heat transfer rates, providing critical data for various applications. These devices often have specific performance metrics that can significantly impact their effectiveness. Recent studies indicate that the precision of heat flux measurement can vary by as much as 30% across different designs. This inconsistency highlights the need for careful selection based on specific project requirements.
In engineering practices, the choice of transducer can affect system performance. For example, sensors with a higher response time may lag in fast-changing thermal environments. This can lead to potential miscalculations in thermal analysis. The materials used, typically thermocouples or thin-film sensors, drastically change the response and sensitivity of measurement. A recent report showed that thin-film sensors tend to provide higher accuracy, especially in dynamic temperature conditions.
**Tip:** Always consider the application before choosing a transducer. Analyze the environment and thermal dynamics of your project. Understand measurement accuracy parameters as they can make a marked difference. Additionally, invest time in calibrating devices properly. Regular maintenance can help mitigate errors. This precaution is often overlooked but is crucial for reliable data.
Top 10 Heat Flux Transducers You Need to Know About
| Transducer Type | Temperature Range (°C) | Heat Flux Range (W/m²) | Accuracy (%) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type K | -40 to 1250 | 0 - 30000 | ±2 | Manufacturing Processes |
| Type J | -40 to 750 | 0 - 25000 | ±3 | Aerospace Testing |
| Thin Film | -50 to 500 | 0 - 10000 | ±1 | Research Experiments |
| Thermal Paste | -20 to 200 | 0 - 15000 | ±2 | Electronics Cooling |
| Fluxmeter | 0 to 1000 | 0 - 20000 | ±5 | Building Energy Studies |
| PCB | -100 to 500 | 0 - 50000 | ±1.5 | Manufacturing Quality Control |
| Membrane | -50 to 100 | 0 - 6000 | ±4 | Fluid Dynamics Research |
| Rod | -100 to 800 | 0 - 40000 | ±3 | Heat Exchanger Testing |
| Surface | -50 to 600 | 0 - 25000 | ±2 | Materials Testing |
| Micro | -200 to 300 | 0 - 5000 | ±2 | Biomedical Applications |
Comparative Analysis: Cost vs. Accuracy in Heat Flux Transducers
In the realm of heat flux transducers, the balance between cost and accuracy is crucial. Industry reports indicate that while highly accurate models can deliver precision readings within ±1%, they also command premium prices. On the other hand, more budget-friendly options often sacrifice accuracy, with margins reaching ±5% or more. This trade-off begs careful consideration from engineers and researchers.
In practical applications, investing in top-tier precision can lead to better data reliability. For example, inaccurate measurements can result in costly design flaws or inefficient processes. A study highlighted that even a 2% error in heat flux can cause a 10% increase in system inefficiency. However, when budgets are tight, it may be challenging to justify these costs.
**Tip:** Always evaluate your project’s needs. If a specific accuracy level is critical, prioritize your budget accordingly. Subsequently, consider alternative funding or project scopes.
Additionally, it's wise to consider long-term benefits versus upfront costs. In some cases, a cheaper model could lead to more expenses down the line due to erratic performance. However, for transient experiments, a less expensive unit may suffice.
**Tip:** Analyze past experiments. Look for patterns in data that could indicate if cheaper alternatives might work. This could save resources without significant accuracy loss.
Future Trends in Heat Flux Transducer Technology and Innovation
The future of heat flux transducer technology is bright. Innovations are emerging rapidly. Sensors are becoming smaller and more efficient. Users can expect higher accuracy in measurements. This is crucial for various applications, such as thermal management and energy systems.
Tips: When selecting a transducer, consider its response time. Fast response ensures accurate data in dynamic environments. Understanding the application requirements is essential for optimal performance.
Another trend is wireless technology. Wireless transducers offer flexibility and ease of use. They reduce cable clutter in installations, but they can be less reliable. Ensuring stable communication is vital. Users might need to re-assess network coverage in their specific setups.
Improving materials is also key. New materials enhance durability and sensitivity. However, some may come at a higher cost. It's worth weighing the benefits against the budget. Make informed decisions to avoid overspending without enhancing performance.
Related Posts
-
Why Heat Flux Sensors Are Essential for Accurate Thermal Measurements
-

Why You Need a Heat Flux Meter for Accurate Energy Measurements
-

Top Strategies for Optimizing Crop Yield with Soil Temperature Sensors
-
What is Thermal Conductivity of Materials Explained with Examples and Applications
-

Best Thermal Conductivity Sensors for Accurate Temperature Measurements
-

Understanding Pyranometers and Their Role in Solar Radiation Measurement