2025 Top 10 Temperature Sensors: The Best Choices for Precision and Performance
As industries worldwide continue to embrace automation and IoT technologies, the demand for accurate and reliable temperature sensors has never been more critical. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the global temperature sensor market is projected to grow from $5.32 billion in 2020 to $7.56 billion by 2025, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.1%. This significant growth underscores the essential role that temperature sensors play in a myriad of applications, ranging from industrial processes to home automation systems.
Experts in the field emphasize the importance of selecting the right temperature sensor to ensure precision and performance. Dr. Emily Carter, a leading researcher at SensorTech, states, "Choosing the appropriate temperature sensor is not just about meeting requirements; it significantly impacts efficiency and safety in any given application." This insight highlights the pressing need for industry professionals to stay informed about the latest developments and innovations in temperature sensor technology.
In this article, we will explore the top 10 temperature sensors in 2025, focusing on their features, performance metrics, and ideal applications. By examining these options, we aim to assist businesses and engineers in making informed decisions in a market increasingly characterized by rapid technological advancements and evolving standards.

Top Features to Look for in High-Performance Temperature Sensors
When selecting high-performance temperature sensors, several key features should be prioritized to ensure precision and reliability. First and foremost, accuracy is critical; opt for sensors that offer minimal deviation from actual temperature readings. High-resolution sensors with fine measurement increments enable more detailed monitoring and can be especially advantageous in environments where slight fluctuations matter, such as in industrial or laboratory settings.
Another important feature is the response time of the sensor. Faster response times contribute to better performance in dynamic environments where temperature changes can occur rapidly. Additionally, consider the sensor's range and operating conditions. It is essential to choose sensors that can function effectively within the specific temperature range required for your application, whether it's extreme cold or high heat environments. Durability and resistance to environmental factors, such as humidity or corrosive substances, further enhance the sensor's longevity and reliability, making it a critical consideration in the selection process.
Comparison of Temperature Sensor Types: Which One is Right for You?
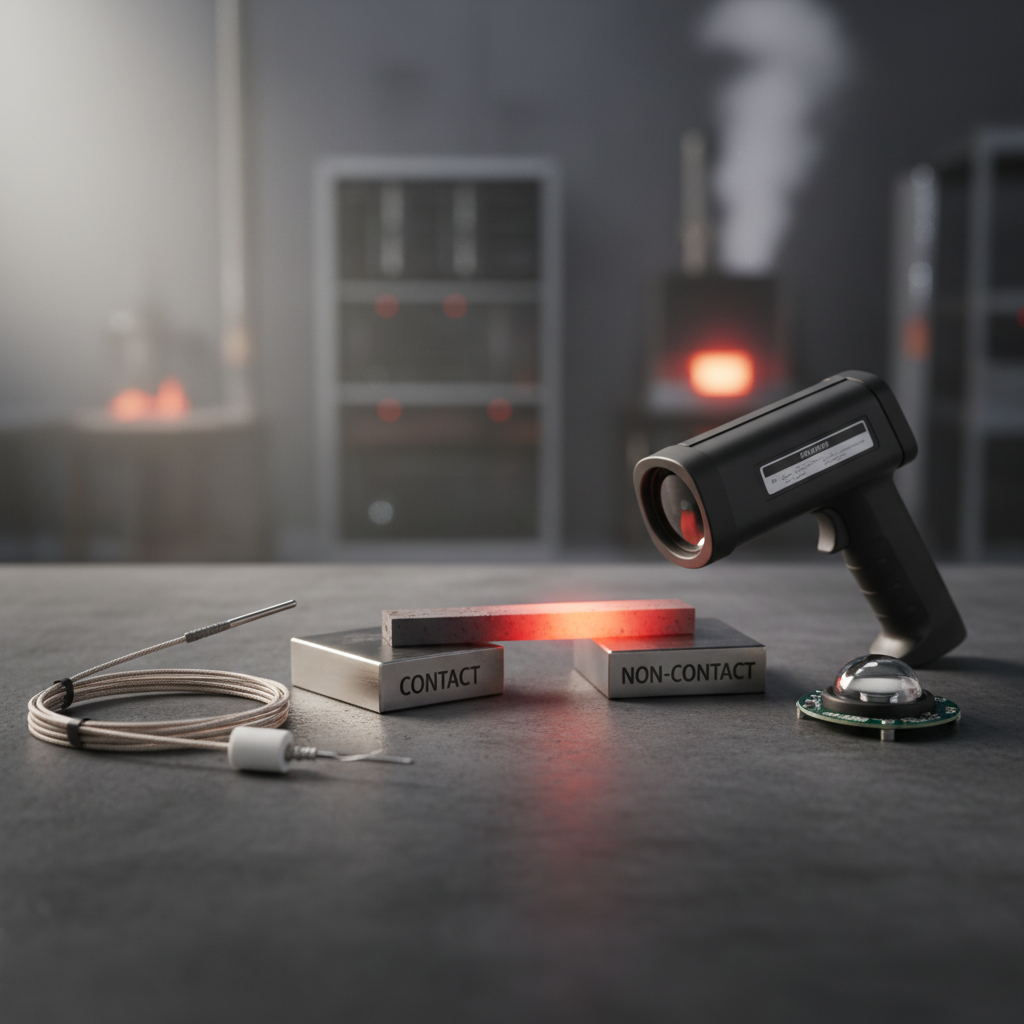

When selecting a temperature sensor for your application, understanding the different types available is crucial to achieving optimal performance. The two primary categories of temperature sensors are contact and non-contact sensors. Contact sensors, such as thermocouples and RTDs, measure temperature through direct contact with the object being measured. They are ideal for applications requiring high accuracy and stability, making them suitable for industrial processes and laboratory environments. Thermocouples, for instance, are known for their wide temperature range and rapid response, while RTDs offer superior precision and linearity.
On the other hand, non-contact temperature sensors, including infrared sensors, measure the thermal radiation emitted by an object to determine its temperature without physical contact. These sensors are particularly useful in scenarios where the object is moving, at high temperatures, or in hazardous environments. They provide quick measurements and are often utilized in medical and automotive applications. When choosing between these sensor types, consider factors such as the operating environment, temperature range, response time, and required accuracy to ensure you select the most appropriate sensor for your specific needs.
Leading Brands of Temperature Sensors in 2025: A Detailed Overview
In 2025, the temperature sensor market has seen remarkable advancements, with several leading brands setting new benchmarks for precision and performance. Brands such as Fluke, Omega Engineering, and Texas Instruments have emerged as frontrunners. These companies focus on integrating cutting-edge technologies, such as IoT connectivity and enhanced data accuracy, to meet the diverse needs of various industries, including healthcare, automotive, and manufacturing. Their sensors not only promise reliability but also offer user-friendly interfaces that simplify data collection and analysis.
When selecting a temperature sensor for your application, consider the specific requirements such as temperature range, response time, and environmental conditions. Additionally, ensure compatibility with your existing systems to streamline integration.
Another important factor is the calibration process; regular calibration improves measurement accuracy and extends the lifespan of these sensors. Look for brands that provide detailed calibration services and support, as this can greatly enhance your operational efficiency and reduce downtime in critical applications.
2025 Top 10 Temperature Sensors Performance Comparison
This chart illustrates the accuracy percentage of the top 10 temperature sensors available in 2025, showcasing their performance in precision measurement.
Innovative Technologies Driving Temperature Sensor Accuracy and Reliability

The landscape of temperature sensors is evolving rapidly, driven by innovative technologies that enhance both accuracy and reliability. Advanced materials and microfabrication techniques are at the forefront of these developments, allowing for miniaturization and improved sensitivity. For instance, MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) technology has enabled the creation of highly precise and compact temperature sensors that can be easily integrated into various applications.
**Tip:** When selecting a temperature sensor, consider the specific application requirements, including temperature range, response time, and environment. Sensors designed with integrated circuit technology often provide better accuracy and are more resilient to environmental factors, making them ideal for demanding conditions.
Another significant innovation comes from wireless technology, which has transformed the way temperature data is collected and transmitted. Wireless sensors reduce the need for cumbersome wiring, providing flexibility in installation and reducing costs. These sensors often utilize advanced algorithms for data processing, ensuring high reliability even in fluctuating temperature conditions.
**Tip:** Ensure that the wireless temperature sensors have a robust communication protocol to maintain signal integrity. Features like redundancy and fail-safes in data transmission can significantly improve system reliability, especially in critical monitoring scenarios.
Key Applications for Precision Temperature Sensors Across Industries
The global temperature sensor market is projected to demonstrate significant growth, reaching an estimated value of $10.52 billion by 2025 and further expanding to $10.71 billion by 2033, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.4%. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for precision temperature monitoring across various industries. Key applications include consumer electronics, automotive electronics, and industrial manufacturing, highlighting the diverse environments where accurate temperature readings are essential. The market is segmented into types such as thermocouples, thermistors, resistance temperature detectors, with both digital and analog sensors playing critical roles in ensuring performance and reliability.
In the realm of industrial applications, advanced technologies such as infrared temperature sensing are enabling smart manufacturing enhancements, particularly in regions like China where production quality is paramount. The rapid adoption of temperature sensors in healthcare further substantiates the market's expansion, as these devices are vital for patient monitoring and diagnosis. With a strong focus on innovation and performance, the temperature sensor market is poised to meet the burgeoning requirements across sectors, ensuring precise control and monitoring become integral to operational efficiency.
2025 Top 10 Temperature Sensors: The Best Choices for Precision and Performance
| Rank | Sensor Type | Temperature Range (°C) | Accuracy (%) | Response Time (s) | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Thermocouple | -200 to 1800 | ±0.5 | 0.1 | Manufacturing, Aerospace |
| 2 | RTD | –200 to 850 | ±0.2 | 0.5 | Food Processing, Pharmaceuticals |
| 3 | Thermistor | -40 to 150 | ±0.1 | 0.05 | Medical Devices, HVAC |
| 4 | Infrared | -70 to 300 | ±1 | <1 | Building Automation, Safety |
| 5 | Bimetallic | 0 to 550 | ±2 | 1 | Industrial Equipment, Heating |
| 6 | Fiber Optic | -200 to 1000 | ±0.5 | 0.2 | Oil & Gas, Power Generation |
| 7 | Solid-State | -55 to 150 | ±0.5 | 0.5 | Consumer Electronics, Automotive |
| 8 | Gas Thermometer | -200 to 500 | ±0.1 | 2 | Research Labs, Calibration |
| 9 | Contact Temperature Sensor | -50 to 300 | ±0.5 | 0.1 | HVAC, Home Appliances |
| 10 | Microscale Temperature Sensor | -40 to 125 | ±0.3 | <0.01 | Biomedical, Environmental Monitoring |
Related Posts
-

5 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Temperature Sensor for Your Business Needs
-

Understanding the Essential Role of Temperature Monitoring Sensors in Modern Industries
-

10 Best High Temperature Sensors for Accurate Measurements in 2023
-

How to Choose the Right Temperature Sensor for Your Specific Application
-

Understanding How Temperature Probe Sensors Revolutionize Home Cooking and Food Safety
-

Understanding Temp Sensors: How They Revolutionize Modern Climate Control Systems