What is Omega Heat Flux Sensor and How Does It Work in Energy Measurement
The need for precise energy measurement has become increasingly vital as industries strive for efficiency and sustainability. Among the devices catering to this need, the omega heat flux sensor stands out due to its accuracy in monitoring heat transfer and energy loss. According to a report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), improving energy efficiency in buildings could reduce global energy demand by 20% by 2040, underscoring the necessity for advanced measurement tools like the omega heat flux sensor.
This sensor operates by quantifying the rate of heat transfer through surfaces, providing valuable data that can aid in optimizing energy consumption. Research indicates that sectors such as manufacturing and HVAC can benefit significantly from employing thermal sensors, with potential energy savings of up to 30% when integrated into existing systems. Utilizing the omega heat flux sensor not only enhances operational efficiency but also supports the growing demand for energy management solutions in various industries, emphasizing its importance in the energy landscape.

What is Omega Heat Flux Sensor? An Overview of Its Role in Energy Measurement
The Omega Heat Flux Sensor is an essential tool in the field of energy measurement, designed to accurately assess the heat transfer occurring over its surface. This sensor operates by measuring the temperature difference across a known thickness of a material, allowing it to calculate the heat flow per unit area. The device typically consists of thermopiles that generate a voltage output proportional to the temperature gradient, facilitating real-time analysis of energy transfer processes.
In energy measurement applications, the Omega Heat Flux Sensor plays a crucial role in various sectors, including building energy efficiency, thermal management systems, and industrial processes. For instance, in building science, it helps in assessing the insulation performance by quantifying heat loss through walls or roofs. By providing precise data on heat flux, the sensor enables engineers and researchers to optimize energy usage, leading to better energy conservation strategies and improved sustainability in designs.
Principle of Operation: How Omega Heat Flux Sensors Measure Thermal Energy Flow
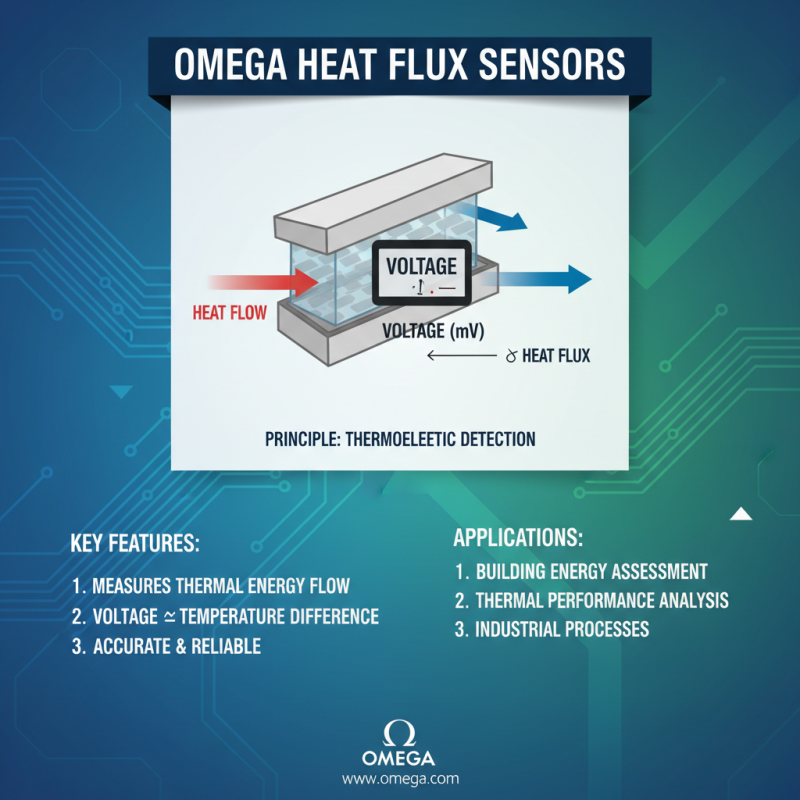
Omega heat flux sensors are essential tools for measuring the flow of thermal energy through materials. These sensors operate based on the principle of thermoelectric detection. When a temperature difference occurs across the sensor's surface, it generates a voltage that is proportional to the heat flux, allowing for precise measurement of thermal energy transfer. This technology is widely used in applications such as building energy assessments, thermal performance analysis, and various industrial processes where heat management is crucial.
The measurement process involves placing the sensor in direct contact with the surface whose heat flux is to be measured. The sensor typically consists of a thermopile, which is made up of multiple thermocouples connected in series. This configuration amplifies the small voltage generated by the temperature differential. The reading obtained from the sensor can be calibrated to account for various environmental factors, ensuring accurate data that reflects the actual energy flow. Through these mechanisms, Omega heat flux sensors play a vital role in optimizing energy efficiency and understanding thermal dynamics in different systems.
Key Technical Specifications: Understanding Sensitivity and Range of Omega Sensors
Omega heat flux sensors are crucial tools used in energy measurement, particularly in assessing thermal performance in various applications. Understanding their key technical specifications, such as sensitivity and range, is essential for effective deployment. Sensitivity refers to the sensor's ability to detect minute changes in heat flux. A higher sensitivity means that the sensor can accurately measure low levels of heat transfer, making it particularly useful in environments where energy efficiency is critical. This characteristic is vital in applications such as insulation performance testing or evaluating heat loss in buildings.
The range of the sensor indicates the maximum and minimum heat flux levels it can accurately measure. A wider range allows for more versatile applications, accommodating both very low and very high levels of heat transfer. This flexibility is beneficial for researchers and engineers who might encounter varying thermal conditions during measurements. Understanding both the sensitivity and range of these sensors enables users to select the appropriate specifications based on their specific measurement needs, ensuring accurate and reliable data for energy assessment and optimization.
Omega Heat Flux Sensor - Data Measurement Overview
This bar chart illustrates the heat flux measurements of different sensors, showcasing their performance in terms of heat transfer efficiency. The data represents the heat flux (in watts per square meter) recorded by each sensor, highlighting variances amongst different configurations.
Applications in Industry: Use Cases for Omega Heat Flux Sensors in Energy Management
Omega heat flux sensors play a crucial role in energy management across various industries by providing accurate and timely measurements of heat transfer. These sensors are essential in applications such as building energy audits, where they help to identify energy loss through walls and ceilings. By using heat flux data, facility managers can pinpoint areas with inefficiencies, leading to better insulation strategies and overall energy savings. This process not only lowers operational costs but also contributes to the sustainability goals of organizations.
In industrial settings, Omega heat flux sensors are utilized for process optimization and control. In manufacturing, for instance, these sensors can monitor thermal processes during material production, ensuring that systems operate within specified temperature ranges. This capability helps to enhance product quality while reducing waste caused by overheating or energy overuse. Additionally, in power generation facilities, accurate heat measurement is vital for performance assessments and predictive maintenance. By analyzing heat flux data, operators can make informed decisions about equipment upgrades and repairs, ultimately supporting more efficient energy management strategies.
Comparative Analysis: Omega Heat Flux Sensors vs. Other Energy Measurement Tools

When it comes to energy measurement, understanding the comparative advantages of Omega heat flux sensors versus other measurement tools is essential for accurate data collection and analysis. Omega heat flux sensors provide specific benefits, such as high sensitivity and precision in measuring heat transfer rates. They are particularly useful in applications involving thermal insulation evaluation, building efficiency analysis, and research in material science. Their ability to quickly respond to changes in thermal conditions makes them a superior choice for real-time monitoring compared to traditional methods.
In contrast, other energy measurement tools, such as thermocouples and infrared sensors, may offer different advantages depending on the specific requirements of the project. For instance, thermocouples are often less expensive and can measure temperatures over a wide range but lack the fine resolution and direct measurement capabilities of heat flux sensors. Infrared sensors can measure surface temperatures without contact, which can be beneficial in some contexts but may miss critical data on heat flow through materials.
Tips: When selecting an energy measurement tool, consider the specific application and environment. For critical heat flow studies, Omega heat flux sensors could provide the precise data needed, while other tools may serve better for cost-effective, broad temperature measurements. Understanding the strengths of each tool will help you make informed decisions that suit your energy measurement needs.
Related Posts
-

Innovative Applications of Omega Heat Flux Sensors in Modern Industries
-

Unveiling the Future of Temperature Sensors at the 138th Canton Fair in 2025
-

Top Strategies for Optimizing Crop Yield with Soil Temperature Sensors
-

Understanding Pyranometers and Their Role in Solar Radiation Measurement
-

Understanding How Temperature Probe Sensors Revolutionize Home Cooking and Food Safety
-

Top 10 Soil Temperature Sensors for Accurate Agriculture Monitoring