What Is a Heat Flow Meter? Understanding Its Importance in Energy Efficiency
Understanding the significance of energy efficiency in today’s world is more crucial than ever. As industries strive to reduce their operational costs and environmental impact, the role of advanced measurement tools has come to the forefront. One such essential tool is the heat flow meter, a device that plays a vital role in measuring thermal energy transfer through materials. By accurately quantifying how much heat is transferred, these meters provide critical data that can enhance energy efficiency strategies across various applications.
The heat flow meter operates by assessing the thermal properties of insulation materials, allowing engineers and builders to make informed decisions about energy conservation. With energy costs rising and environmental regulations becoming stricter, understanding the function and importance of heat flow meters has never been more relevant. This introduction to heat flow meters will explore their design, functionality, and the pivotal role they play in optimizing energy usage and promoting sustainable building practices. As we delve deeper, we will uncover how the implementation of these devices can lead to significant improvements in energy efficiency, benefiting both the economy and the planet.
What Is a Heat Flow Meter?

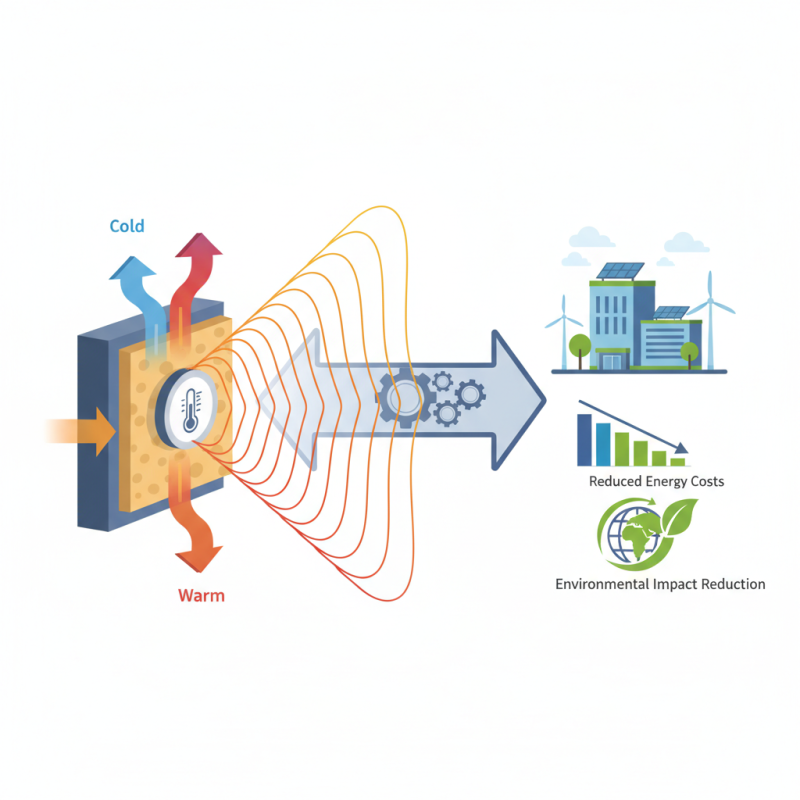
A heat flow meter is an essential instrument used to measure the rate of heat transfer through materials. It operates based on the principles of thermodynamics, capturing the variation in temperature across a material's surface. By placing sensors on either side of the material, the meter can quantify the heat flow, allowing for an accurate assessment of thermal performance. This measurement is crucial in various applications, including building insulation assessment, industrial processes, and energy management systems.
Understanding how a heat flow meter functions is vital for engineers and architects who aim to improve energy efficiency. The data collected from these meters provides insights into how well a building or material retains heat, which can inform design choices and renovation efforts. Through this analysis, professionals are better equipped to identify areas for improvement, helping to reduce energy consumption and lower costs. Additionally, by incorporating heat flow meters in research and development, companies can innovate and develop materials with enhanced thermal properties, further contributing to sustainability goals.
The Working Principle of Heat Flow Meters
Heat flow meters are crucial instruments used to measure the transfer of heat through various materials, which is essential for assessing energy efficiency in buildings and industrial processes. The working principle of a heat flow meter revolves around the accurate detection of temperature differences across a given material. Typically, a heat flow meter comprises two temperature sensors embedded in a substrate that is surrounded by a thermally insulating material. By measuring the temperature difference between the two sensors, the device can calculate the heat flow rate in watts per square meter.
The operation of a heat flow meter relies on the principles of thermodynamics. When there is a temperature gradient across the material, heat energy will flow from the warmer side to the cooler side. The heat flow meter quantifies this thermal energy transfer by utilizing the relationship defined by Fourier's law of heat conduction, which states that the heat transfer rate is directly proportional to the temperature difference and the area through which the heat is passing. This precise measurement helps in determining the thermal resistance of materials, enabling engineers and architects to design more energy-efficient structures and systems. By optimizing insulation materials and overall thermal performance, buildings can significantly reduce energy consumption, leading to cost savings and a lower environmental impact.
What Is a Heat Flow Meter? Understanding Its Importance in Energy Efficiency
| Dimension | Data |
|---|---|
| Measurement Range | -10°C to 100°C |
| Accuracy | ±0.5% of reading |
| Data Logging Interval | 1 minute |
| Power Supply | Battery operated (20 hours) |
| Communication Interface | USB & Bluetooth |
| Application Areas | HVAC, Building Energy Management, Industrial Processes |
| Cost | $300 - $1000 |
Applications of Heat Flow Meters in Energy Efficiency

Heat flow meters are essential tools for measuring heat transfer in various applications, playing a crucial role in enhancing energy efficiency across multiple sectors. In construction and building materials testing, they are employed to evaluate insulation properties, ensuring that structures are energy-efficient and meet required thermal performance standards. By accurately assessing how heat moves through different materials, builders can make informed decisions on insulation types and installation, ultimately reducing energy consumption in heating and cooling systems.
In the industrial sector, heat flow meters are increasingly utilized to monitor and optimize processes where heat management is critical. For instance, in manufacturing plants, these devices help identify heat loss points in machinery, allowing for timely maintenance or upgrades that enhance operational efficiency. Furthermore, in energy auditing, heat flow meters provide valuable data for assessing building energy performance, enabling organizations to implement targeted improvements that can lead to substantial cost savings and reduced environmental impact. Overall, the applications of heat flow meters are vital for promoting sustainable practices and improving energy efficiency in both residential and industrial settings.
Benefits of Using Heat Flow Meters in Building Management
Heat flow meters (HFMs) play a critical role in building management, particularly in enhancing energy efficiency. These devices measure the rate of heat transfer through a building element, such as walls or roofs, providing valuable insights into thermal performance. According to a report by the International Energy Agency, buildings are responsible for approximately 40% of global energy consumption. By using heat flow meters, facility managers can pinpoint areas of heat loss and implement targeted improvements, leading to significant energy savings. Studies suggest that optimizing insulation based on HFM data can reduce energy costs by up to 30%.
One of the standout benefits of utilizing heat flow meters is their ability to provide real-time monitoring of thermal performance. This not only aids in immediate adjustments but also supports long-term energy management strategies. The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers emphasizes the importance of precise measurements, stating that effective insulation can lead to a reduction in heating and cooling loads, contributing to lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Tips: When implementing heat flow meters, ensure that they are calibrated correctly for accurate readings. Regular maintenance and data analysis are essential for maximizing their effectiveness—consider integrating your meter readings with building management systems for streamlined monitoring. Also, training staff on interpreting the data can enhance decision-making and lead to improved energy management practices.
Heat Flow Meter Usage in Building Management
This bar chart illustrates the heat flow measured in various buildings, highlighting the effectiveness of heat flow meters in monitoring energy efficiency. Proper monitoring can lead to significant energy savings and improved building management strategies.
Future Trends in Heat Flow Measurement Technology
The landscape of heat flow measurement technology is evolving rapidly, driven by the increasing demand for energy efficiency across various sectors. As industries are striving to meet stringent sustainability goals, advancements in heat flow meters are becoming paramount. According to a report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), about 40% of global energy consumption is attributed to buildings, emphasizing the need for precise heat measurement to optimize energy usage.
Emerging technologies are focusing on integrating advanced sensors and IoT capabilities into heat flow meters, which allow for real-time monitoring and data analytics. This integration can lead to significant cost savings and reduced energy waste.
Moreover, the adoption of machine learning algorithms in data processing is anticipated to enhance the accuracy of heat flow measurements. A recent study by Grand View Research projects that the global market for heat flow meters will witness substantial growth, with a CAGR of over 7% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is fueled by increasing awareness of energy management practices and rising utility costs.
Future heat flow meters are expected to feature enhanced connectivity options, enabling seamless integration with existing building management systems. As a result, building operators can implement more effective energy strategies, leading to improved sustainability outcomes in line with upcoming regulations and standards.
Related Posts
-

How to Select the Right Heat Flow Meter for Your Industrial Needs
-

Ultimate Guide to Mastering Thermal Conductivity Sensors for Enhanced Performance
-
Exploring Innovative Applications of Thermal Conductivity Sensors in Modern Technology
-

Understanding Temp Sensors: How They Revolutionize Modern Climate Control Systems
-
Top 10 Temperature Probe Sensors for Accurate Cooking and Laboratory Use
-

2025 Top Thermal Conductivity Meter Guide for Optimal Performance and Accuracy