How to Choose the Right Heat Flux Meter for Your Measurement Needs
When it comes to accurately measuring heat transfer within various systems, selecting the right heat flux meter is crucial for obtaining reliable data. Heat flux meters are devices designed to quantify the rate of heat transfer per unit area, providing essential insights for applications in engineering, building construction, and thermal performance assessment. Given the diverse range of available options, choosing a suitable heat flux meter can be daunting for professionals and researchers alike.
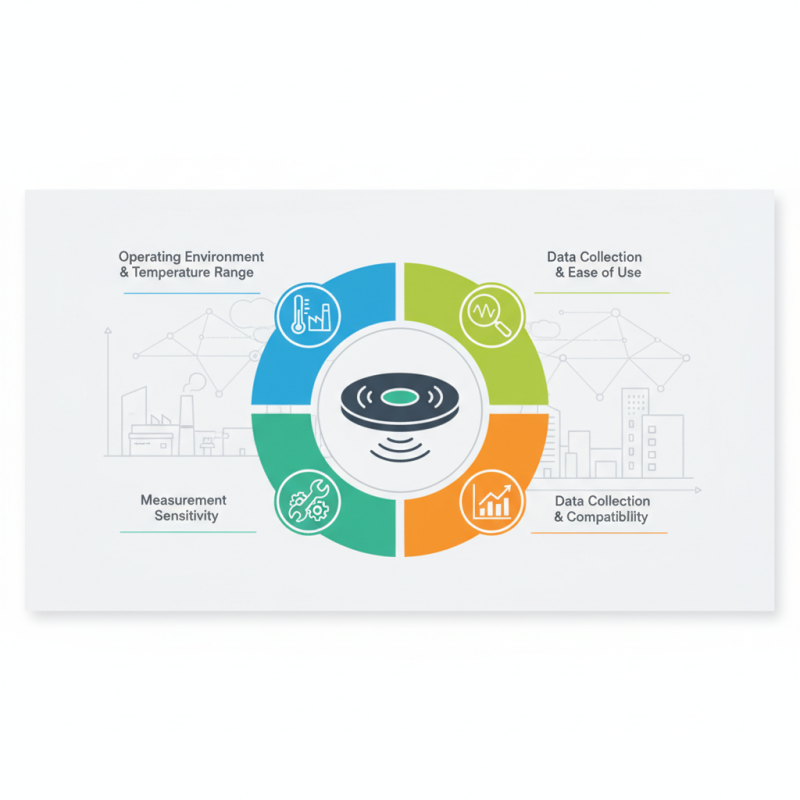
Understanding the specific measurement needs is the first step in making an informed decision. Factors such as the operating environment, temperature range, and the required sensitivity of measurements play a significant role in determining the most appropriate heat flux meter for the task at hand. Additionally, users should consider the installation process, ease of data collection, and compatibility with existing systems to ensure a seamless integration that meets their objectives.
Ultimately, selecting the right heat flux meter not only enhances the accuracy of measurements but also contributes to the overall efficiency of thermal management in various applications. By carefully evaluating the unique requirements of each project, users can make informed choices that lead to successful outcomes in their heat transfer studies.
Understanding Heat Flux Measurement: Basics and Importance
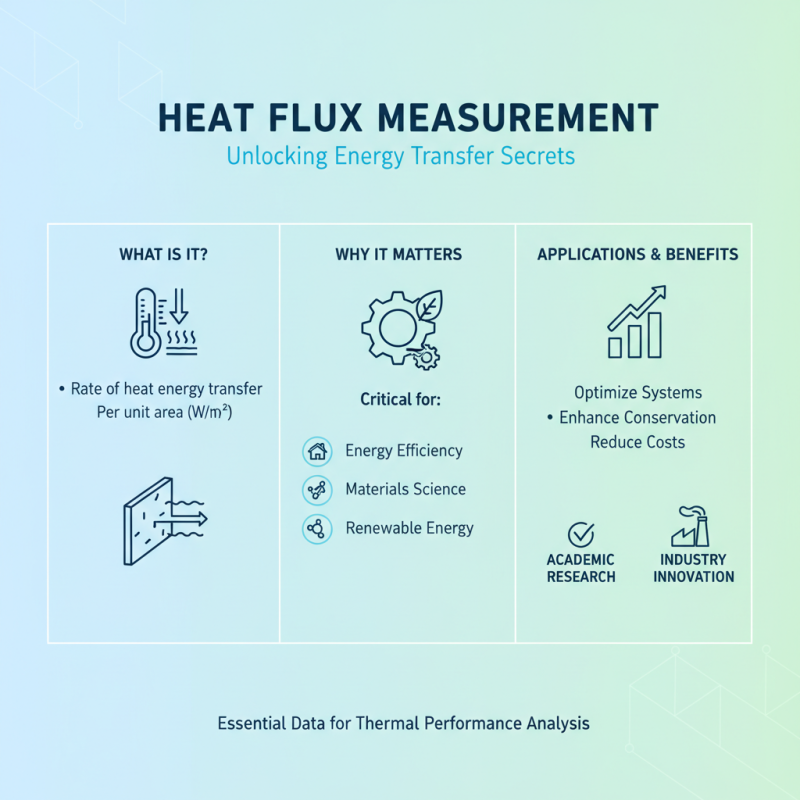
Heat flux measurement is a critical aspect of various scientific and engineering applications, providing essential data for understanding energy transfer in thermal systems. By quantifying the rate of heat energy transfer per unit area, heat flux meters enable researchers and engineers to analyze thermal performance, which is pivotal in fields like building energy efficiency, materials science, and renewable energy technologies. These measurements facilitate the optimization of systems to enhance energy conservation and reduce costs, making them invaluable for both academic research and practical industry applications.
The importance of heat flux measurement extends beyond mere data collection; it plays a vital role in ensuring the reliability and efficiency of thermal systems. Accurate heat flux readings enable the identification of heat losses and gains in structures, contributing to better insulation practices and energy management strategies. Furthermore, in experimental setups, precise heat flux measurements are crucial for validating theoretical models and improving material properties. Understanding the fundamentals of heat flux and its measurement techniques is essential for professionals dedicated to advancing technology and fostering sustainable practices in their respective fields.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting a Heat Flux Meter
When selecting a heat flux meter, it's crucial to consider several key factors that align with your specific measurement needs. First and foremost, the required sensitivity and range of measurement play a significant role. According to a 2021 industry report by the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE), the recommended sensitivity for accurate heat flux measurements typically falls within 10-100 mW/m², making it vital to choose a meter that can provide consistent results within this range for your intended application.
Another essential aspect to evaluate is the temperature response time of the heat flux meter. Different materials and construction methods can lead to varied response characteristics. A study in the Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry found that meters with a faster response time can significantly improve the accuracy of transient measurements, which is particularly important in dynamic environments like building energy simulations or industrial processes. Ensuring that your chosen meter suits the expected thermal dynamics will help in capturing precise data critical for analysis.
Lastly, consider the installation and calibration requirements associated with the heat flux meter. A user-friendly setup with easily understandable calibration procedures can save time and reduce the likelihood of measurement errors. As highlighted in a report by the European Association for Renewable Energies, ease of integration with existing systems can also enhance overall efficiency. By prioritizing these factors, you can ensure that your heat flux meter will meet your measurement needs effectively.
Heat Flux Meter Selection Criteria
Types of Heat Flux Meters: Features and Applications
When selecting a heat flux meter, understanding the different types available and their specific features and applications is essential. There are primarily two categories of heat flux meters: the thin-film sensors and the ceramic types.
Thin-film sensors are known for their high sensitivity and rapid response times, making them ideal for applications where precise measurements are crucial, such as in research laboratories and aerospace testing. They are typically used in situations where the heat flux rates vary rapidly, allowing for real-time monitoring and detailed thermal analysis.
On the other hand, ceramic heat flux meters are characterized by their robustness and durability. These sensors can withstand harsh environmental conditions, making them suitable for industrial applications like building insulation assessments and energy audits. Their ability to handle high temperatures and pressure means they can be deployed in a range of settings, from manufacturing plants to field testing in construction projects.
By considering the specific features of each type, users can make informed decisions tailored to their measurement needs, ensuring accurate and reliable heat flux data for their projects.
Accuracy and Calibration: Ensuring Reliable Measurements
When selecting a heat flux meter, accuracy and calibration are paramount for obtaining reliable measurements. According to the International Society of Heat Transfer (ISHT), the accuracy of heat flux meters can vary significantly, often between ±1% to ±5% of the reading. Ensuring that your chosen meter meets stringent calibration standards can drastically reduce measurement errors and enhance the quality of data collected during experiments or production processes. Regular calibration against known standards is critical, especially in professional settings where precision is essential.
To maintain accuracy, it's vital to follow the manufacturer's guidelines closely. An annual calibration is generally recommended, but specific environments may necessitate more frequent checks. Additionally, using calibration services that are accredited can provide further assurance of the instrument's reliability. For instance, calibration against primary standards ensures traceability, which is essential for applications demanding precision.
**Tips:** Always record the calibration date and results to track the performance of your heat flux meter over time. Moreover, consider the environmental conditions in which measurements will be taken, as factors like temperature and pressure can influence readings. Regular training on operating procedures can also ensure that all users understand how to optimize the device's performance and interpret data correctly.
How to Choose the Right Heat Flux Meter for Your Measurement Needs - Accuracy and Calibration: Ensuring Reliable Measurements
| Model | Measurement Range (W/m²) | Accuracy (%) | Calibration Method | Price ($) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model A | 0 - 5000 | ±2 | Factory Calibration | 250 |
| Model B | 0 - 10000 | ±1.5 | Field Calibration | 400 |
| Model C | 0 - 2000 | ±3 | Lab Calibration | 150 |
| Model D | 0 - 7500 | ±2.5 | Automatic Calibration | 300 |
| Model E | 0 - 3000 | ±2.8 | Digital Calibration | 220 |
Budget and Investment: Balancing Cost with Measurement Needs
When selecting a heat flux meter, one of the primary considerations is the delicate balance between budget constraints and the specific measurement needs of your project. Industry reports indicate that a significant percentage of users (over 60% according to recent surveys) often opt for cost-effective devices that may lack advanced features or precision. This can lead to inaccuracies in measurements, particularly in environments where precise thermal management is critical, such as in aerospace and energy sectors, where even minor discrepancies can result in substantial financial losses or operational inefficiencies.
Investing in a higher-end heat flux meter can offer substantial returns, particularly when dealing with specialized applications. Reports from leading research bodies show that utilizing high-quality meters can enhance measurement accuracy by up to 25%. This improvement can be particularly crucial in research and development sectors, where precise data informs design decisions. While the initial investment might be higher, the long-term benefits of accurate data collection and potential savings from avoided errors can outweigh these costs, making it a wise consideration for businesses aiming to optimize their thermal systems. Overall, thoughtful investment in heat flux measurement technology is key to achieving reliable and actionable data aligned with project goals.
Related Posts
-

5 Compelling Reasons Why Heat Flow Meters Are Essential for Energy Efficiency in Industries
-

How to Select the Right Heat Flow Meter for Your Industrial Needs
-

How to Optimize Energy Consumption with Advanced Heat Flow Meter Technology
-
Why Heat Flux Sensors Are Essential for Accurate Thermal Measurements
-

Top 5 Solar Radiation Sensors: Maximize Your Solar Energy Efficiency
-

Top 5 Best Temperature Probe Sensors for Accurate Cooking and Brewing