How to Choose the Right Thermal Conductivity Meter for Your Needs in 2025
In the realm of material science and engineering, the ability to measure thermal properties accurately is of paramount importance. One of the critical instruments for this purpose is the thermal conductivity meter. As we progress into 2025, the advancements in technology and the growing demands for precision in various industries necessitate the careful selection of a thermal conductivity meter that suits specific needs. Whether in research laboratories, manufacturing settings, or construction sites, understanding how to choose the right thermal conductivity meter can significantly impact the quality of results and overall efficiency.
Thermal conductivity meters vary widely in terms of design, capabilities, and applications, making it essential for users to assess their requirements meticulously. Factors such as measurement range, sensitivity, ease of use, and data management features play a vital role in the selection process. Additionally, as industries evolve, the importance of selecting a meter that complies with the latest standards and offers reliable and reproducible results cannot be overstated. This guide aims to empower professionals and researchers alike to navigate the myriad options available and choose the therapy conductivity meter that best aligns with their operational needs, ensuring optimal performance and accuracy in their work.

Understanding Thermal Conductivity and Its Importance in Measurement
Thermal conductivity is a critical property of materials that measures their ability to conduct heat. In various industries, including manufacturing, construction, and electronics, understanding thermal conductivity is essential for selecting the right materials for insulation, heat sinks, and other applications where heat transfer is significant. According to a report from the International Journal of Thermal Sciences, effective thermal management can improve energy efficiency by up to 30% in industrial processes. Therefore, accurately measuring thermal conductivity not only ensures product performance but also enhances sustainability efforts.
When selecting a thermal conductivity meter, it is essential to consider the application requirements carefully. For instance, if your needs include measuring low thermal conductivity materials like insulators, a laser flash apparatus may be more suitable. In contrast, for metals or higher conductivity materials, a guard heat flow meter could be more appropriate. Always refer to the ASTM standards pertaining to the specific materials you are testing to ensure compliance and accuracy.
**Tips:** Before purchasing a thermal conductivity meter, evaluate the range of materials you will be measuring and choose a device with the appropriate measurement technology. Additionally, ensure that the device can operate under the environmental conditions of your testing location, as temperature and humidity can significantly affect measurements. Investing time in selecting the right instrument based on precise measurements will pay dividends in product quality and performance.
Types of Thermal Conductivity Meters Available in 2025

In 2025, the market for thermal conductivity meters has expanded to accommodate a variety of measurement needs across industries. The most common types of thermal conductivity meters include transient and steady-state devices. Transient thermal conductivity meters are typically utilized for rapid testing scenarios where quick measurements are essential. According to recent industry reports, these devices can provide accuracy within 5% error margins, making them ideal for applications in materials research and quality control processes.
On the other hand, steady-state thermal conductivity meters, such as guarded hot plate and heat flow meters, are favored for their precision in determining thermal properties over longer testing periods. A study conducted by the Thermal Properties Society in early 2025 indicated that these instruments could achieve an accuracy of better than 3%, which is crucial for industries requiring exact thermal measurements, like construction and thermal insulation. Additionally, portable thermal conductivity meters are gaining traction, offering flexibility and ease of use for field testing, which is particularly valuable for building energy assessments and environmental studies.
As professionals look to choose the right thermal conductivity meter, understanding the distinctions between these types is vital. The data suggests that the increasing demand for precise thermal management solutions across various sectors will continue to push innovation in the design and functionality of these instruments, ensuring they meet the evolving needs of users in 2025 and beyond.
Key Features to Look for When Selecting a Thermal Conductivity Meter
When selecting a thermal conductivity meter in 2025, it is essential to focus on key features that align with your specific application requirements. One critical aspect is the measurement range and accuracy. According to a report by the International Society of Thermal Conductivity, modern meters now offer a range of up to several hundred watts per meter-kelvin (W/m·K), with some high-end models achieving an accuracy of ±1% or better. This precision is vital for industries such as materials science and electronics, where even minor deviations in thermal conductivity can lead to significant performance impacts.
Another important feature to consider is the ease of use and portability of the device. With a shift towards more field-based measurements in sectors like construction and energy efficiency, many new models come equipped with user-friendly interfaces and built-in data storage. Industry data indicates that devices with advanced connectivity options, such as Bluetooth and Wi-Fi, are becoming increasingly popular, allowing for real-time data sharing and analysis. This trend not only enhances the user experience but also facilitates better integration with other testing equipment, making it easier to obtain comprehensive thermal performance evaluations.
Finally, durability and environmental resistance should not be overlooked, especially in diverse operating conditions. Research from the Materials Testing Institute shows that meters exposed to extreme temperatures or humidity levels require robust designs to maintain accuracy over time. In 2025, selecting a thermal conductivity meter with enhanced casing and moisture-resistant features will be crucial for long-term reliability, ensuring that your investment is protected against harsh environments while maintaining consistent performance.
Thermal Conductivity by Material Type (2025)
Factors Influencing the Accuracy of Thermal Conductivity Measurements
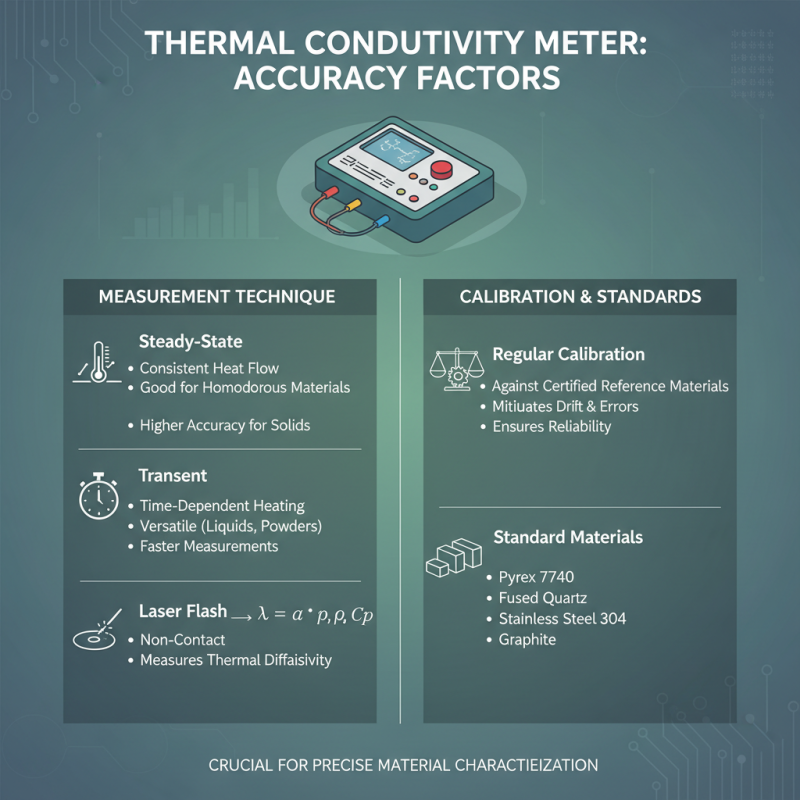
When selecting a thermal conductivity meter, understanding the factors that influence the accuracy of thermal conductivity measurements is crucial. One significant factor is the measurement technique employed by the device. Different methods, such as steady-state, transient, or laser flash techniques, can yield varying degrees of accuracy based on the material and the specific application. Additionally, the calibration of the meter plays a pivotal role in ensuring precise measurements. Regular calibration against standard materials can help mitigate errors and improve reliability.
Another essential aspect is the environmental conditions during measurement. Factors like temperature and humidity can affect the readings, especially for materials that are sensitive to moisture or heat. Ensuring a controlled environment can greatly enhance the accuracy of the results. Users should also consider the sample size and shape, as irregular materials might introduce further variability.
**Tips:** When choosing a thermal conductivity meter, always review the specifications for measurement techniques and calibration processes. Ensure that the device can accommodate the materials you’re testing, and consider investing in a temperature-controlled testing environment to improve measurement consistency. Regularly assess your equipment and adopt standardized procedures for best results.
Applications of Thermal Conductivity Meters Across Different Industries
Thermal conductivity meters play a crucial role across various industries, providing essential data that informs product development, quality control, and compliance with safety standards. In the construction sector, for instance, these meters are used to measure the thermal properties of insulation materials. Accurate readings help manufacturers ensure that their products meet energy efficiency regulations and improve the overall thermal performance of buildings. With growing concerns about energy consumption and environmental impact, choosing the right meter is vital for architects and builders who prioritize sustainability.
In the electronics industry, thermal conductivity meters assist in assessing the heat dissipation capabilities of components such as semiconductors and circuit boards. Proper thermal management is critical in maintaining performance and extending the lifecycle of electronic devices. By ensuring that materials used in these products possess optimal thermal conductivity, manufacturers can prevent overheating and enhance reliability. Similarly, in the food processing sector, these meters are employed to evaluate the thermal properties of packaging materials, contributing to better preservation and safety of food items. The versatility of thermal conductivity meters across these applications underscores the importance of selecting the appropriate model to meet specific industry needs and challenges.
How to Choose the Right Thermal Conductivity Meter for Your Needs in 2025 - Applications of Thermal Conductivity Meters Across Different Industries
| Industry | Common Applications | Key Features to Look For | Typical Measurement Range (W/m·K) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Insulation Material Testing | High Accuracy, Portable Design | 0.01 - 10 |
| Electronics | Semiconductor Testing | Fast Response Time, Wide Range | 0.1 - 1000 |
| Food Industry | Thermal Analysis of Food Products | Non-destructive Testing, Ease of Use | 0.001 - 5 |
| Automotive | Material Testing for Thermal Insulation | Durability, Extended Range | 0.02 - 50 |
| Energy | Insulation Performance Monitoring | Energy Efficiency Metrics, In-field Readings | 0.1 - 20 |
Related Posts
-

How to Choose the Right Thermal Conductivity Meter for Your Application
-
Understanding the Impact of Thermal Conductivity on Material Selection in Engineering
-

Best Thermal Conductivity Sensors for Accurate Temperature Measurements
-

The Ultimate Guide to PV Monitoring: Boosting Solar Efficiency for Global Buyers
-

The Role of Solar Irradiance Sensors in Optimizing Renewable Energy Systems
-

7 Key Reasons Thermal Conductivity Testing is Essential for Modern Manufacturing Success