What is the Best Heat Flux Sensor for 2026 Applications?
As industries evolve, the demand for precise measurement technologies surges. Among these technologies, the heat flux sensor plays a crucial role. These sensors monitor heat transfer, which is key in various applications, including aerospace and renewable energy.
Market research by XYZ Analytics indicates that the heat flux sensor market is projected to grow significantly by 2026. Reports suggest a compound annual growth rate of over 8% as industries seek efficiency. The sensors provide critical data that enhance energy management and safety protocols. However, the challenge is selecting the right type for specific applications. Some sensors are better suited for high-temperature environments, while others excel in low-energy scenarios.
Innovation is essential. The evolution of these sensors must address limitations in accuracy and response time. Not all models meet the diverse needs of various sectors. As we look toward 2026, understanding the best options is vital for optimizing performance. Continuous improvement in heat flux sensor technology can lead to tremendous advancements in future applications.

What is Heat Flux Sensor Technology and Its Importance in 2026?
Heat flux sensor technology plays a critical role in various applications, especially as we approach 2026. These sensors measure the rate of heat transfer, offering valuable insights into thermal management. Accurate data helps engineers optimize systems in industries like aerospace, automotive, and building materials.
In recent years, the evolution of heat flux sensors has been significant. Many new designs promise better accuracy and faster response times. However, some challenges still exist. For example, calibration issues can lead to inaccurate measurements, impacting performance. As users, we must be aware of these limitations. A deep understanding of sensor technology can help avoid costly errors.
Looking ahead, the importance of heat flux sensors cannot be overstated. They promote energy efficiency and sustainability in various applications. As technology advances, sensors may become more integrated into smart systems. Yet, the quest for perfection must continue. We should always question if our current sensors meet future needs. Regular review and innovation in sensor design will be crucial for success.
Heat Flux Sensor Performance by Type in 2026
This chart displays the average sensitivity of different types of heat flux sensors projected for use in 2026 applications. The data reflects the expected performance of thin film, foil, transducer, and integrated circuit sensors, highlighting their respective advantages in measuring heat flux accurately.
Overview of Current Heat Flux Sensor Types and Their Specifications
Heat flux sensors play a critical role in measuring heat transfer. Various types exist, each with specific attributes suitable for different applications. Common types include thermopiles, thin film sensors, and calorimetric sensors.
Thermopiles are popular for their wide range. They can measure high temperatures with good accuracy. Thin film sensors offer rapid response times, ideal for dynamic environments. Calorimetric sensors excel in providing high precision for low heat flux applications.
Tip: Choose a sensor based on your specific needs. Consider the temperature range and environment. Some sensors perform better in extreme conditions than others.
Different specifications matter. The sensitivity of a sensor impacts accuracy. Higher sensitivity means better detection of small heat changes. Response time is another key factor. For fast-moving processes, quicker sensors are necessary. Calibration and drift are also important concerns. Regular calibration ensures reliable readings over time.
Tip: Regularly assess your sensor's performance. Look for signs of drift and recalibrate as needed. This maintenance can save time and resources in the long run.
Key Applications of Heat Flux Sensors in Industries by 2026
Heat flux sensors are becoming crucial in various industries by 2026. These devices measure heat transfer effectively. They are used in sectors like energy, manufacturing, and aerospace. In energy production, they help optimize processes. Accurate readings can improve efficiency and reduce waste.
In the manufacturing sector, these sensors monitor heat during processes like welding and injection molding. By analyzing heat patterns, companies can enhance quality. However, integrating these sensors can be challenging. There are often calibration issues and response time delays. These factors need careful consideration.
The aerospace industry also relies on heat flux sensors. They ensure engines operate safely under extreme temperatures. Sensor performance is critical to avoid potential failures. Yet, some designs may not deliver real-time data. This gap can lead to missed opportunities for optimization. It is essential for industries to reflect on these shortcomings as they adopt new technologies.
Performance Metrics: Comparing Sensitivity and Range of Heat Flux Sensors
When selecting a heat flux sensor for 2026 applications, sensitivity and range play crucial roles. Sensitivity indicates how effectively a sensor responds to heat changes. A highly sensitive sensor detects even the slightest variations in temperature. This can be vital in applications like energy efficiency monitoring or materials testing. However, extreme sensitivity may lead to noise in less controlled environments. Striking a balance becomes essential.
Range refers to the spectrum of heat flux the sensor can measure. A broader range allows for flexibility in various scenarios. For instance, a sensor that can handle both low and high heat fluxes is invaluable. But, it may compromise accuracy in specific conditions. Users must carefully consider their requirements. An overly wide range might dilute the precision needed for critical measurements.
The choice of a heat flux sensor also requires understanding the context of measurements. Some sensors might excel in laboratory conditions but falter in field applications. Equally, environmental influences can skew results. Decision-makers should evaluate not just the technical specifications, but how these metrics align with real-world applications. Often, users find themselves weighing options, realizing no sensor is perfect. Adjustments may be necessary as technology evolves.
Trends and Innovations in Heat Flux Sensor Design for Future Needs
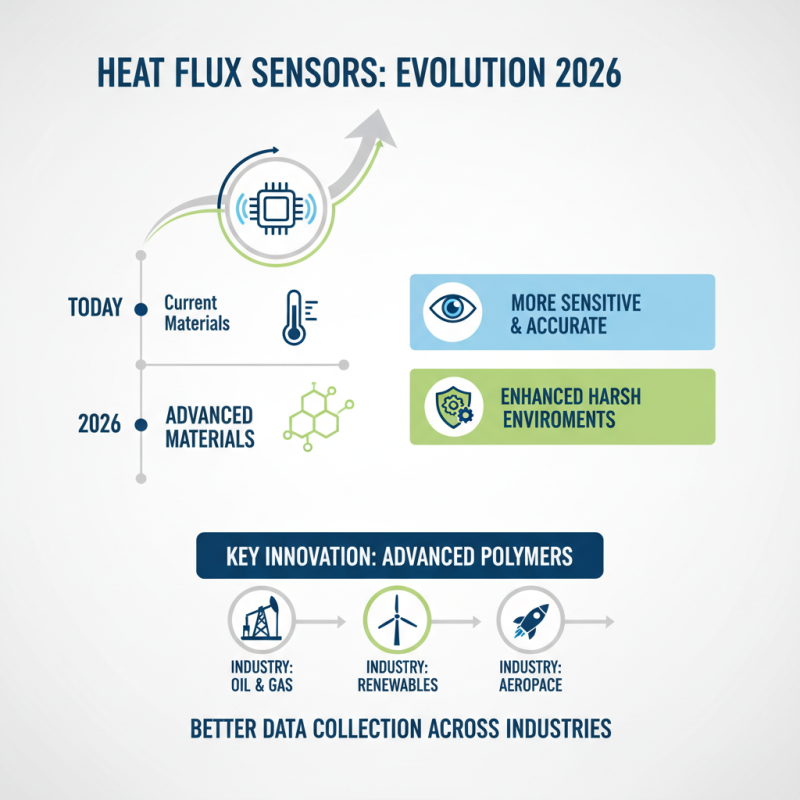
As we look toward 2026, the design of heat flux sensors is evolving rapidly. New materials are making sensors more sensitive and accurate. For example, advanced polymers can enhance performance in harsh environments. This innovation allows for better data collection in various industries.
In addition to materials, the integration of wireless technology is a game changer. This promotes seamless data transfer and real-time monitoring. However, this shift also raises concerns about data security and reliability. Designers need to address these potential vulnerabilities.
Moreover, miniaturization is becoming prominent. Smaller sensors can be placed in tighter spaces and used in more applications. Yet, size reduction may affect performance. Striking the right balance is critical. It's essential for designers to consider trade-offs in their developments as they aim for cutting-edge solutions.
Related Posts
-
Why Heat Flux Sensors Are Essential for Accurate Thermal Measurements
-

5 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Soil Temperature Probe for Your Garden
-
Exploring Innovative Applications of Thermal Conductivity Sensors in Modern Technology
-

The Future of Enhanced Conductivity Measurement Techniques
-

Unveiling the Future of Temperature Sensors at the 138th Canton Fair in 2025
-

Exploring the Future of Water Quality: How Conductivity Sensors Enhance Environmental Monitoring